Cannabis deficiencies: How to fix them
Learn what cannabis deficiencies are and how you can address them.
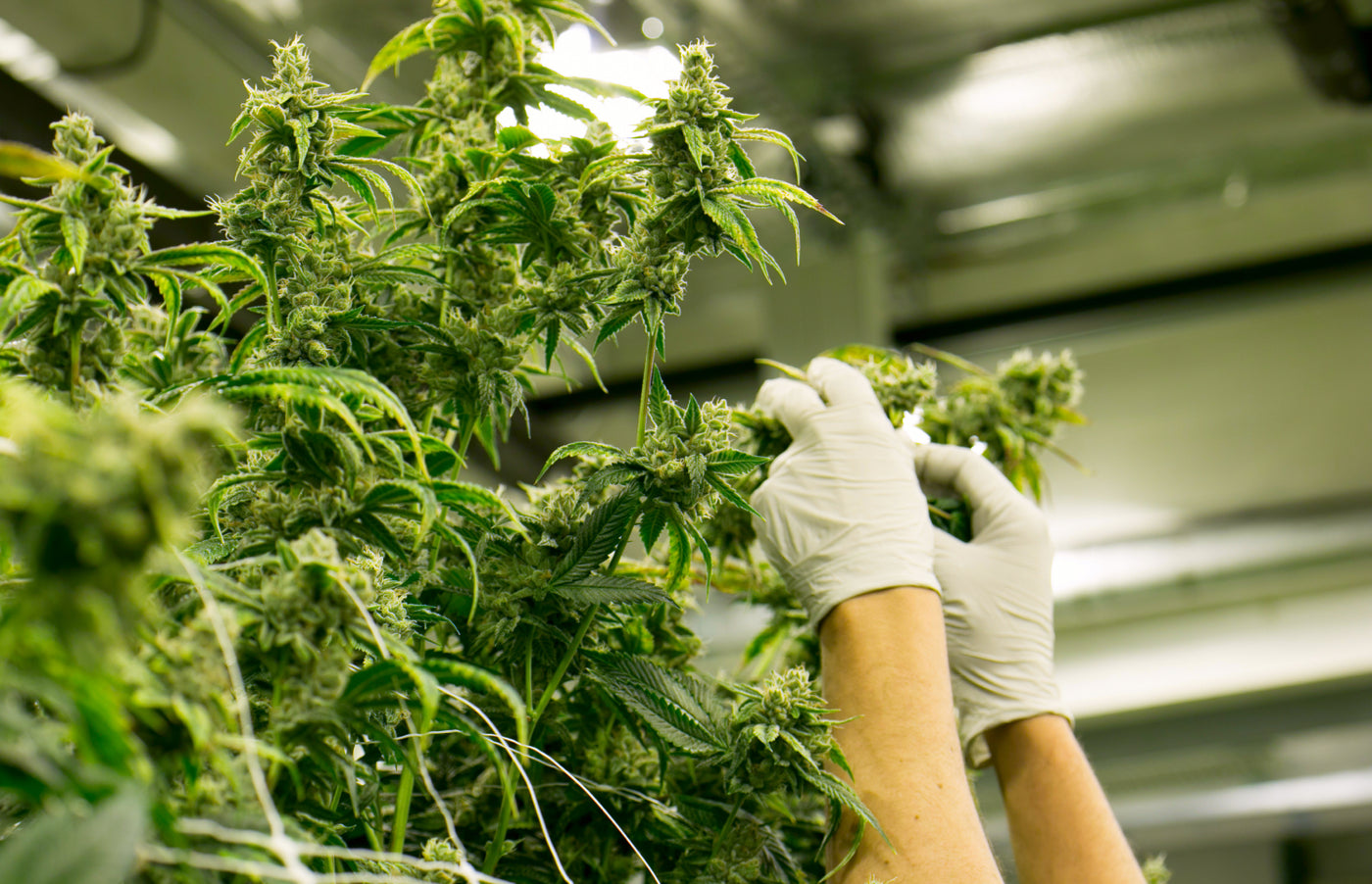

The Cannabis sativa plant is notoriously tough and capable of growing in a wide range of environments and conditions. But while the volume of cannabis cultivation is rapidly rising from gardens to greenhouses, quality control is increasingly important when creating products worth buying.
In other words, the minimum methods and practices aren’t meeting consumer expectations or industry standards any longer. To procure the highest quality plants and create hemp extracts with precise formulations and effects, growers must address common cannabis deficiencies and know exactly how to fix them.
Let’s walk through the various cannabis deficiencies that affect plant appearance and overall product quality so that you can get the best yields and make the most of your investments.
What are cannabis deficiencies?
Cannabis deficiencies can result from a lack of nutrients or another imbalance that negatively impacts the growth and health of a cannabis plant. In minor cases, deficiencies result only in aesthetic changes to the plant that don’t affect the quality of its cannabinoids and therapeutic effects.
In more severe cases, these deficiencies can amount to a decrease in the quality of the hemp itself, from the flowering buds of the cannabis plant to the leaves, stalks, stems, and other components used to obtain hemp extracts. While the cannabis plant is resilient in most environments, major deficiencies can result in the death of the plant and leave you empty-handed.
Nutrients are the primary subject of interest when discussing cannabis deficiencies, but many other factors come into play. From pH levels to air quality and maintenance practices, you may encounter small deficiencies that eventually turn into bigger problems for your plants.
Whether you’re growing cannabis for personal use or leveraging larger-scale operations for a business venture, you’ll want to be able to identify these deficiencies and address them quickly.
The good news is that a quick diagnosis and response can usually save a cannabis plant from an unfortunate fate and bring you back on track in the cultivation process. Keep in mind that different strains of cannabis require unique forms of treatment and support, as some are more sensitive or prone to deficiencies than others.
Also, consider the possibility that excess nutrients can cause issues that may appear to be deficiencies but are still harmful to the health of the plant. Excess and deficiency are two sides of the same coin that must be accounted for in cannabis cultivation.
What are some common types of cannabis nutrient deficiencies?
There are five major types of cannabis nutrient deficiencies that growers and manufacturers must consider when cultivating plants. While some deficiencies manifest with colors and spots, others can only be detected by observing growth patterns and comparing them with the optimal development cycle of your plant.
Let’s check out the five most common types of cannabis nutrient deficiencies and explain what you should look for to make an accurate evaluation.
Potassium
Potassium is among the few essential nutrients needed for cannabis growth, and deficiencies can cause dramatic problems for plants both visually and structurally.
As a powerful electrolyte, potassium controls the opening of the “pores” in the cannabis leaves and stalks, allowing light, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water to flood in for nourishment. Potassium also activates ATP production, which is key to creating glucose from photosynthesis.
With too little potassium, the cannabis plant becomes unable to absorb enough of these vital components for growth. It also results in poor photosynthesis, which leads to further malnourishment and developmental issues.
Calcium
Although calcium is considered a secondary nutrient for cannabis, it’s still a vital nutrient that promotes growth and protects plants from disease and other issues. The main role of calcium in cannabis is the absorption of nutrients, thanks to the regulation of cell membrane permeability.
Calcium also helps with the movement of nutrients throughout the cannabis plant, which is why a calcium deficiency can lead to more severe deficiencies of other kinds.
In addition to these necessities, calcium helps cannabis plants build resistance to diseases, pests, heat stress, and other abrupt environmental changes. The right amount of calcium makes cannabis plants more resilient in terms of their response to the growing environment.
Magnesium
Magnesium may only be a micronutrient, but it’s vital to the growth and health of cannabis plants from stage one. Because magnesium is a key part of the chlorophyll molecule, it’s mostly concentrated in the leaves of the plant, which are responsible for the absorption of light in photosynthesis.
Robust and green cannabis leaves mean the magnesium is flowing, along with strong enzyme production and flowering. However, it’s often difficult to detect a magnesium deficiency because they tend to take more than a month to appear with visual signs.
Phosphorus
Another essential nutrient, phosphorus, plays a role in many critical plant functions. Phosphorus is needed in relatively large amounts during all phases of plant development, from root growth and stem strength to resistance against frost, heat, diseases, and pests.
Phosphorus also helps the cannabis plant absorb water and other nutrients more efficiently and boosts the production of glucose from photosynthesis. When the flowering phase begins, phosphorus is needed to increase bud quality and yield, as well as regulate seed germination for continued production.
Thankfully, phosphorus is abundant in many natural forms, from compost and coffee grounds to phosphate rocks and even manure. A phosphorus deficiency can be addressed relatively quickly at all stages, so keep an eye out for common symptoms.
Nitrogen
The final primary nutrient for cannabis plants is nitrogen, and it’s needed for the entire plant life cycle. Nitrogen is vital for vegetative growth during initial plant development but is also needed during the flowering stage in smaller amounts.
Nitrogen supports photosynthesis as well as plant resistance across the board, ensuring a healthy and sturdy plant from start to finish. Fast-growing cannabis strains need a lot of nitrogen, making nitrogen deficiency one of the most common types.
How can you recognize cannabis deficiencies?
With so many factors and nutrients at play, recognizing the exact causes of cannabis deficiencies is a tall task, especially for rookie growers. However, a few common signs indicate various deficiencies that allow growers to narrow down the possible causes and make the right adjustments.
Here are the top three signs that cannabis plants are deficient in nutrients and some suggestions for which compounds might be responsible.
Yellowing
Cannabis leaves are meant to range in color from light green to rich dark green when the plant begins to mature. Yellow leaves are a common sign that some form of nutrient deficiency is happening behind the scenes.
Generally, yellowing leaves mean that chlorophyll production is lower than average, meaning that the plant is not able to perform photosynthesis properly. Before long, this leads to a malnourished plant, as the leaves cannot produce the sugars needed to power ongoing growth and flower development.
Closely observe plants for signs of yellowing before photosynthesis and nutrient production are further affected, especially in new leaves.
Curling leaves
Common sense suggests that curling leaves result from proximity to heat sources like lamps, and this isn’t necessarily wrong. However, growers need to look beneath the surface at why this problem persists, and it usually means that the plant lacks key nutrients to retain its resilience to heat, along with structural issues.
Hot temperatures and light burns might be the simple answers, but plants with curling leaves may also lack nutrients like calcium, potassium, and magnesium. Overwatering or adding too much fertilizer can also backfire and lead to curling, so finding the middle ground is always the goal to combat curling in new leaves or older leaves.
Abnormal coloration
Yellowing may be the most common type of discoloration in cannabis, but there are many more signs that manifest in this way. Brown spots on leaves are a common signal of nitrogen shortages or may even signify the presence of pests or diseases.
Whether it’s dark streaks, spots, or even overly dark green leaves, growers need to closely monitor colors and prepare to make changes quickly.
What contributes to cannabis deficiencies?
Nutrient levels are just one part of the equation when assessing cannabis deficiencies. Here are some other factors that may contribute to problems when growing.
pH levels
The optimal pH level for cannabis development is between 5.8 and 7.0, though some growers suggest a narrow range up to 6.4 or even lower. Cannabis thrives in slightly acidic soil conditions, so growers should constantly monitor pH at every stage.
In alkaline soil, plants may experience stunted growth or develop brown spots on leaves, while overly acidic conditions will cause yellowing and other forms of toxicity. Fortunately, there are many ways to alter acidity to the ideal levels without compromising plant health.
Water supply
Watering is a universal challenge in plant growth, and cannabis cultivation is no exception. A lack of water will quickly dry out thirsty plants, while too much hydration can drown roots and obstruct nutrient intake.
Observe growth rates, look for drooping leaves, and monitor other changes to see if overwatering is an issue. You’ll quickly see drying and brittle leaves if underwatering becomes a problem.
Soil composition
Cannabis soil is a talked-about subject, but it is quite simple in reality. Most soils are rather forgiving, and you’re probably better off focusing on variables that give you more control and insight. If you stick with dark, rich, and relatively loose soil for cannabis, this will likely take you far.
How can you address cannabis deficiencies?
Once you’re able to detect and diagnose cannabis deficiencies, it’s time to take action and remedy the situation. While you may not have perfect insight regarding what’s happening to your plants, the following suggestions will give you some options to take control.
Monitor pH
Many cannabis deficiencies start with acidity, so this should be your first order of business when addressing problems like discoloration, wilting, or growth issues.
Check your soil’s pH at least once per day and make sure it’s in the recommended range. From there, you can add certain nutrients or water plants to influence the levels in either direction. Compounds like phosphoric acid will decrease pH, while lime or baking soda will make it rise.
Only add small amounts of these compounds to push pH in either direction since plants are highly sensitive to such changes.
Incorporate fertilizer
Fertilizers can be a grower’s best friend when cultivating cannabis, especially when addressing nutrient deficiencies. Fertilizers vary widely in composition and purpose, so don’t just pick a product blindly and hope for the best.
Look for fertilizers that are designed for the particular issues you face or the stage of growth that your plants are at. Remember that nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium are the “big three,” but there are many other secondary nutrients to account for.
Start composting to improve soil composition
Composting is a great way to naturally boost soil composition while keeping risk factors from fertilizers relatively low. Composting allows you to utilize scraps from your kitchen or garden to enrich the soil and help cannabis plants overcome deficiencies.
This is a good general nutrient solution to employ when growing cannabis, but it might not be practical when facing major problems in shorter time frames. Use composting as a way to boost macronutrients in soil rather than to quickly address deficiency symptoms.
The bottom line
Plant deficiencies are part of the game when growing cannabis, whether in soil or via hydroponic methods. It’s best to learn about them early on and figure out how to deal with them, as this will ensure your crops become incrementally better each time. Healthy plants mean more cannabinoids, terpenes, and more benefits for users.*
Combatting deficiencies might seem like a never-ending game at first, but before long, you’ll be able to spot common issues and anticipate problems ahead of time. Whether you’re making CBD tinctures or selling high-quality cannabis flower, this information is sure to help sooner than later.*
With this knowledge and a few useful tools at your disposal, you can produce quality hemp products and save yourself a lot of trouble down the road.
Sources:
Pathogens and Molds Affecting Production and Quality of Cannabis sativa L. | Frontiers
Understanding the Significance of pH in Cannabis Cultivation | mg Magazine