CBD vs. CBG: Differences, benefits, uses, & more
Learn the basics of CBD and CBG, including their differences and benefits.
Medically Reviewed by: Dr. Caley Scott, ND
The cannabis plant is loaded with beneficial compounds, some with overlapping benefits and uses. Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are two cannabinoids that share many similarities and are often found together in whole-plant hemp extracts.
But while CBD and CBG tend to go hand in hand, they also feature some key differences that determine how they affect the body. To get the most from your hemp extracts and other cannabis products, it helps to know the upsides of each compound so you can utilize them correctly in your day-to-day.
Let’s explore the similarities, differences, and uses of CBD vs. CBG so you can make the right picks and reap the full range of cannabis benefits.
What is CBD?
CBD is a naturally occurring compound in the cannabis plant and one of the most abundant cannabinoids. CBD has seen a rapid rise in popularity and production in recent years following a series of studies and breakthroughs highlighting its possible benefits and wide applications.
CBD products come in many varieties, including CBD isolates–also called CBD oil. However, the most effective formulations are hemp extracts which contain high concentrations of CBD and other beneficial cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids of the cannabis plant.*
While early iterations of CBD products were simple in concept and structure, more recent hemp extracts are complex. They contain robust cannabis profiles and feature extra ingredients to promote the entourage effect and provide further benefits.*
CBD products are also diverse in format and method of delivery, ranging from tinctures and gummies to gel caps, creams, lotions, and more. With the federal legalization of CBD under the 2018 Farm Bill, CBD research and economic incentives have only increased, leading to a thriving industry with endless possibilities in the health and wellness world.
How does CBD work?
CBD works by interacting with a neural network in the human body known as the endocannabinoid system. The ECS has been identified in nearly all mammal vertebrate species, encompassing neurotransmitters throughout the nervous system, including in the brain and various organs and systems like immune response, digestion, and muscle recovery.*
On a chemical level, CBD interacts with cannabinoid receptors known as CB1 and CB2 receptors, which support a range of biological functions such as mood, motivation, memory, energy levels, and even metabolic health.*
CBD works differently depending on the other chemicals active in the particular product, due to the entourage effect of THC and additional plant compounds.
What are the key benefits of CBD?
The benefits of CBD are vast, and users will experience different effects based on the shape of the user's endocannabinoid system. The most common effect of CBD is that it produces a sense of calm, and reduced feelings of discomfort or tension.*
This is ideal for individuals who experience discomfort throughout the day, whether in stress, physical tension, or emotional ups and downs (I think we can agree this is most of us). CBD users often report a feeling of soothing and relaxing clarity from taking CBD, which can support a range of other health benefits and goals.*
CBD can also help get the body ready for sleep and improve your ability to get a full night’s rest. With sleep deprivation being such a widespread issue, more people are turning to CBD to improve their approach to quality rest.*
Finally, CBD has been known to support other systems of the body, like skin and hair health, plus bone and joint strength.* This could allow users to be more active and help them recover from activity quicker to pursue their fitness goals.*
Does CBD have psychoactive properties?
CBD does not have intoxicating, psychoactive properties—despite being a cannabinoid like THC. While these two compounds come from the same plant and interact with similar receptors, they are fundamentally different in structure and do not trigger the same response from the CB1 and CB2 receptors.*
CBD might help to regulate things like mood, memory, and emotional resilience, but you won’t get the intoxicating “high” effects as you would expect from smoking marijuana or taking a THC-heavy edible.*
The lack of intoxicating effects in CBD means that the compound is far more versatile for daily use and can be paired with a wide range of supplementary ingredients. While you might avoid THC at work or before physical activity because of its sometimes drowsy effects, CBD does not detract from your ability to perform.*
There may be a time and place to enjoy THC and its psychoactive effects, but CBD offers the many advantages of cannabis without having to roll the dice with an uncomfortable intoxicating experience.*
What is CBG?
CBD is the most talked-about cannabis compound next to THC, while CBG tends to take a back seat. That’s because CBG is less abundant in the cannabis plant, and its effects have not been studied as closely as the big brothers THC and CBD.*
Nevertheless, CBG is an intriguing compound with many potential benefits, although its use cases may be slightly more relevant to niche products than CBD.*
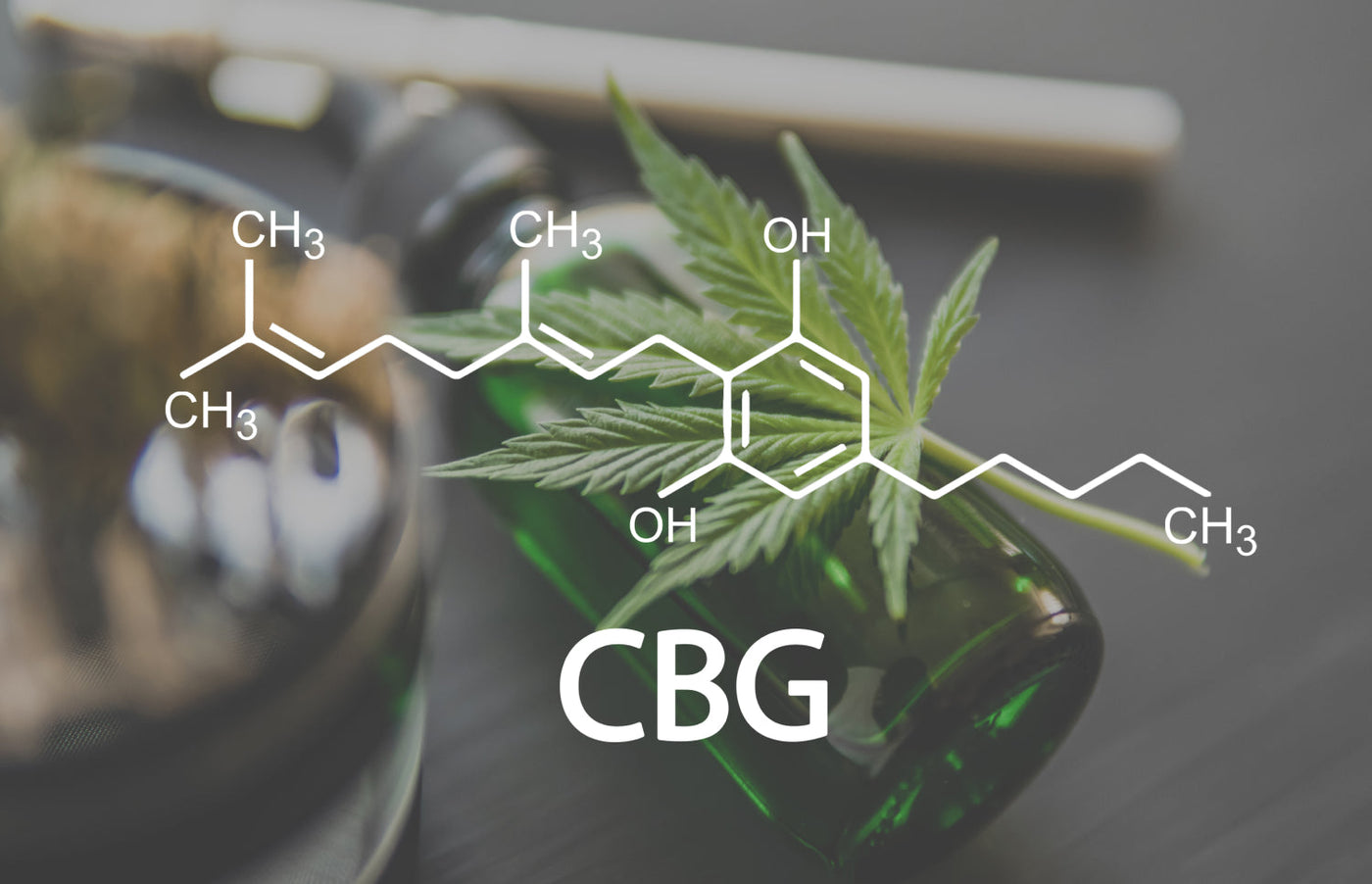
The most unexpected fact about CBG is that its acidic form, CBGA, is the original source of all other cannabis compounds, including CBD, THC, and others—earning it the nickname “the mother of all cannabinoids”. When CBGA breaks down due to oxygenation and other reactions, other cannabinoids take form, while only a small amount of CBG is left behind.*
This means that CBG is one of the least common cannabinoids in the plant, at least in the majority of common cannabis strains. Now that researchers have identified some compelling benefits of CBG, companies are looking to develop strains with naturally higher CBG concentrations.*
CBG may not be the most abundant cannabinoid—but it has earned the attention of scientists, big pharma, entrepreneurs, and cannabis users—making it worth taking a closer look.
How does CBG work?
CBG works in similar ways to other major cannabinoids, interacting with receptors in the endocannabinoid system and helping to regulate certain functions in the body. CBG binds directly to the CB1 and CB2 receptors, unlike CBD, which interacts with these receptors more passively. This suggests that CBG could be a more efficient compound for achieving certain wellness effects.
CBG can work by consuming a tincture, a gummy, or another form of edible for direct absorption into the system.
You may find less variety in terms of CBG product formats. Still, CBG formulations are on the rise, and you can always look at lab reports and COAs to see how much CBG is in each serving of your favorite hemp extract product.
Also, remember the role of the entourage effect with products that emphasize CBG. Hemp extracts with CBG tend to feature other cannabinoids because the compound is naturally less abundant. This is good news for tapping into the entourage effect and getting the benefits of the whole cannabis plant rather than an isolated cannabinoid.*
What are the key benefits of CBG?
The benefits of CBG may seem similar to CBD at first glance, but there are key differences that should inform when and how you use CBG.
The primary appeal of CBG is its ability to support focus and clarity, which are key to maintaining concentration on the task at hand and avoiding distractions. This makes CBG an attractive option for busy professionals or people juggling multiple daily tasks.*
Users also report that CBG has an invigorating, energizing effect, especially in contrast to CBD or THC. While those well-known cannabinoids may be better for relaxation, CBG might be the “get things done” alternative you’ve been looking for.*
CBG might not spike adrenaline or stress like caffeine, and its effects are considerably more gentle and balanced. Still, it offers a great way to utilize cannabis beyond the typical route of calm and relaxation.*
As more info comes to light about CBG and its energizing properties, it’s clear why interest in the compound continues to rise.*
Does CBG have psychoactive properties?
CBG does not have psychoactive properties, making it more similar to CBD than THC in this way. CBG may interact differently with the ECS than other compounds, but it does not intoxicate the mind or body. This contributes to the appeal of CBG for morning or daytime use, rather than a “chill-out” option like THC.*
While CBG might not be a psychoactive substance, its does have the ability to uplight your state of mind—especially when included in hemp extracts utilizing the entourage effect. Hemp extracts with CBG, CBD, and even trace amounts of THC can produce more benefits for the mind and body than taking a single cannabinoid on its own.*
The key is to find a CBG product that specifically emphasizes this compound, with other cannabinoids like CBD or CBC to make the most of each serving.*
What are the key differences between CBD and CBG?
CBD and CBG are more closely related than any variation of THC, but they still feature some differences to consider. They differ in chemical structure and are found in different levels based on the cannabis strain in question, for example.*
They also interact differently with the ECS and produce unique benefits, making them better suited for certain situations. Here’s a closer look at the differences between CBD and CBG so you can make the right pick for you.
Abundance in the cannabis plant
CBD and CBG are on opposite ends of the spectrum regarding abundance in the cannabis plant. While CBD can be found in very high concentrations—up to 40% in some cases—it’s rare to find a natural cannabis strain with more than 2% CBG by volume.
This is mainly due to the process by which CBGA breaks down and how quickly CBG degrades as the plant material oxidizes and ages. While CBD and THC retain their structure successfully with curing and drying processes, CBG continually decreases as the plant life cycle continues.*
This difference emphasizes the importance of finding a CBG-specific product to reap its benefits. Thankfully, more products put CBG in the spotlight as researchers spark interest in its capabilities.
Noted benefits
CBD is considered an all-encompassing cannabinoid for general wellness, relaxation, and keeping the body in mind in balance. It can be used at any time and is highly adaptive, meaning its benefits will change based on the stresses and environmental factors you experience at the time.*
CBG, on the other hand, is more of a niche compound for energy, focus, and invigoration. These products tend to be marketed as daytime supplements and are best used in your morning routine, along with coffee or tea. Some like to incorporate a second serving for a midday pick-me-up.
Of course, everyone responds slightly differently to each cannabinoid. Take note of your unique experience with these compounds so you can the learn the advantages of each for your body.
CBG vs. CBD: Major vs. Minor Cannabinoids
CBD is considered a major cannabinoid due to its abundance in cannabis, meaning it’s also widely studied and easily accessible. In contrast, CBG (cannabigerolic acid) is a minor cannabinoid, present in much smaller amounts, making it rarer and more expensive to produce.
This distinction impacts their availability, cost, and research focus. While CBD is well-known for its broad therapeutic uses, CBG offers unique benefits like cognitive support and heart health support, despite being less studied.
Both cannabinoids contribute to the entourage effect, where major and minor cannabinoids work together to enhance the overall therapeutic impact of cannabis.
Are there any risks associated with CBD and CBG?
Both CBD and CBG have very few side effects associated with them, but it is possible to experience minor side effects — though they are rare and generally mild.
Side effects of CBG may include dry mouth or dry eyes and changes in appetite, while CBD is occasionally associated with drowsiness or nausea. Starting with a low serving size and choosing high quality products can help reduce the likelihood of unwanted side effects.
These cannabinoids may also interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners. We recommend checking with a healthcare provider before adding CBD or CBG to your routine if you’re taking any prescription medications.
When to look for products with CBG
When optimizing your morning cannabis regimen, a CBG-rich hemp extract is the way to go. Sunmed creates formulations that put CBG first, including our Broad Spectrum Rise Gummies with 25 mg total cannabinoids per serving.* The gummy format is familiar and easy to take at home or on the go.
For a fast-acting option, our Full Spectrum Neuro Water Soluble is versatile and can be added to any beverage for a morning boost. It features our CBG + CBD formula, plus our signature PowerTERP blend with black pepper, juniper, and other plant terpenes for added effects.*
If immune support is your goal in the morning, these Full Spectrum Immune+ Capsules have CBGA and CBDA balanced with vitamin C and other ingredients for energy and well-being. This is a great pick for cold winter months or when traveling.*
The bottom line
CBD and CBG are often grouped together as non-psychoactive cannabinoids, but these two compounds have some key differences that should be acknowledged in the hemp space.
CBG may be harder to find, but when you find the right formula, you may find it useful for your morning or midday routine. Meanwhile, anytime CBD products are great for staying calm and in control no matter what life throws at you.
When browsing hemp extracts and structuring your CBD lifestyle, be sure to know the benefits of each compound and use them in the right situations for the best results.
Sources:
The Origin and Biomedical Relevance of Cannabigerol | NIH
The Pharmacological Case for Cannabigerol | NIH
Cannabigerol Overview | ScienceDirect
Cannabis, cannabinoids, and health | PMC
Is Cannabidiol a Safe and Effective Sleep Aid? | Sleep Foundation
Cannabidiol use and effectiveness: real-world evidence from a Canadian medical cannabis clinic | PMC
Cannabidiol: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online