CBG for discomfort: Does it work? A look at the research
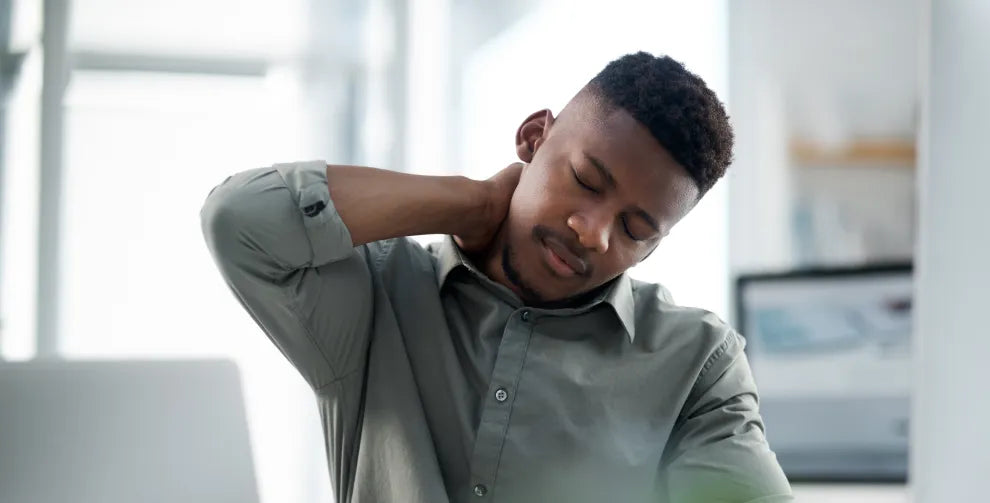

As interest in cannabinoids grows, cannabigerol (CBG) has emerged as a promising compound for wellness, with some research suggesting it may play a role in managing discomfort.
Unlike its more popular counterparts, THC and CBD, CBG is non-psychoactive and is often considered a "minor" cannabinoid.
Despite its lower concentration in cannabis plants, recent advancements in extraction technology have allowed for more concentrated CBG products, which are now more accessible.
So, how effective is CBG for discomfort relief? In this article, we examine the research on CBG's potential for easing discomfort and explore how it interacts with the body.
What is CBG?
CBG, or cannabigerol, is one of the many cannabinoids found in cannabis. Known as the "mother" or "stem cell" cannabinoid, CBG is the precursor to major cannabinoids like THC, CBD, and CBC.
As the cannabis plant matures, enzymes convert CBG into these other cannabinoids, leaving only trace amounts of CBG in the mature plant. This transformation is why CBG was once rare in cannabis products, though recent developments in selective breeding and extraction techniques have made CBG more accessible.
How does CBG interact with the body?
CBG, like other cannabinoids, interacts with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates various functions such as pain perception, mood, immune response, and sleep. While CBG does not bind strongly to CB1 and CB2 receptors (the main ECS receptors), it has shown affinity for other receptors and enzymes involved in discomfort and tension.
Research suggests that CBG may activate alpha-2 adrenergic receptors, which play a role in regulating discomfort and tension, and may also influence TRPV1 receptors, known to mediate the sensation of discomfort in the body.
What is the science behind CBG for discomfort?
There are a few key reasons why CBG might be beneficial when it comes to easing feelings of discomfort and tension.
One of the primary mechanisms through which CBG may support discomfort relief is through its soothing effects. Studies have shown that CBG has potential to work as a calming, soothing agent, which could make it useful for temporary discomfort or tension in the body.
By working to soothe feelings of discomfort at their source, CBG may offer a natural way to help manage tension and irritation, making it a promising addition to wellness routines aimed at soothing bodily discomfort.
Comparing CBG to CBD for discomfort
Both CBG and CBD have gained attention for their potential relieving properties, but they work through slightly different mechanisms. CBD is known for its soothing effects and ability to potentially interact with serotonin receptors, which may enhance emotional wellness and alleviate discomfort.
CBG, on the other hand, focuses more on receptors directly linked to discomfort and enzymes that interact with the inflammatory response.
While CBD has been widely researched for discomfort, early findings suggest that CBG may offer similar benefits, potentially making it a complementary option. Some wellness products combine CBG and CBD to create a more balanced effect through the entourage effect, which is the theory that cannabinoids work better together than in isolation.
Are there potential side effects of using CBG for discomfort?
While CBG is generally considered safe, users should be aware of potential side effects, especially when using high amounts.
Some common side effects of CBG include:
- Dry mouth: Similar to other cannabinoids, CBG may reduce saliva production, resulting in dry mouth.
- Drowsiness: CBG's calming effects may cause drowsiness, especially when taken in high doses.
- Digestive discomfort: In rare cases, CBG may cause mild digestive issues.
As with any wellness product, starting with a low dose is recommended to assess individual tolerance. It's also advisable to consult a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement, particularly for individuals who are new to cannabinoids or who have existing medical conditions.
How to use CBG for discomfort
CBG can be used in various forms to help manage temporary discomfort, including tinctures, capsules, and topicals.
Each form offers unique benefits:
- Tinctures: CBG tinctures provide a fast-acting method for relief as they are absorbed quickly under the tongue. Tinctures are versatile and allow for easy dose adjustment.
- Capsules: CBG capsules offer a convenient and controlled way to take CBG, ideal for users who prefer precise dosing.
- Topicals: Topical CBG products, such as creams and balms, can be applied directly to areas of discomfort, providing targeted relief for muscle and joint tension.
When choosing a product, consider your specific needs. For whole-body support, tinctures and capsules may be beneficial, while topicals offer localized relief. Full spectrum products that include multiple cannabinoids can offer the entourage effect, potentially enhancing CBG's soothing properties.
The future of CBG for discomfort
As research into CBG continues, its potential as a source of natural relief is becoming clearer. Preliminary findings suggest that CBG may provide unique benefits by targeting certain receptors and enzymes, making it a valuable cannabinoid for those seeking natural approaches to discomfort.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the scope of CBG's effects and how it may best be used in therapeutic settings.
The bottom line
CBG's potential for discomfort is backed by early research, showing promise in reducing inflammation and interacting with receptors. While CBG is not a cure-all, its unique properties make it a valuable addition to cannabinoid-based wellness products.
From soothing support to potential tension relief, CBG is becoming an attractive natural option. As research evolves, individuals seeking alternative ways to manage discomfort may find that CBG provides a safe and effective solution.
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Sources:
Cannabigerolic Acid | Science Direct
Acute Cannabigerol Administration Lowers Blood Pressure in Mice | Frontiers