CBD for Migraines: What the Science Says
Learn the basics of how CBD works in the body, what to know about the role of the ECS in migraines, and how CBD may help with this guide.

Key Takeaways:
- CBD is a non-intoxicating compound from the hemp plant that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS).
- Migraines involve recurring episodes of head and neck tension that can be accompanied by light sensitivity, nausea, or other discomfort.
- CBD is being studied for its potential ability to help with migraines, but research is ongoing.
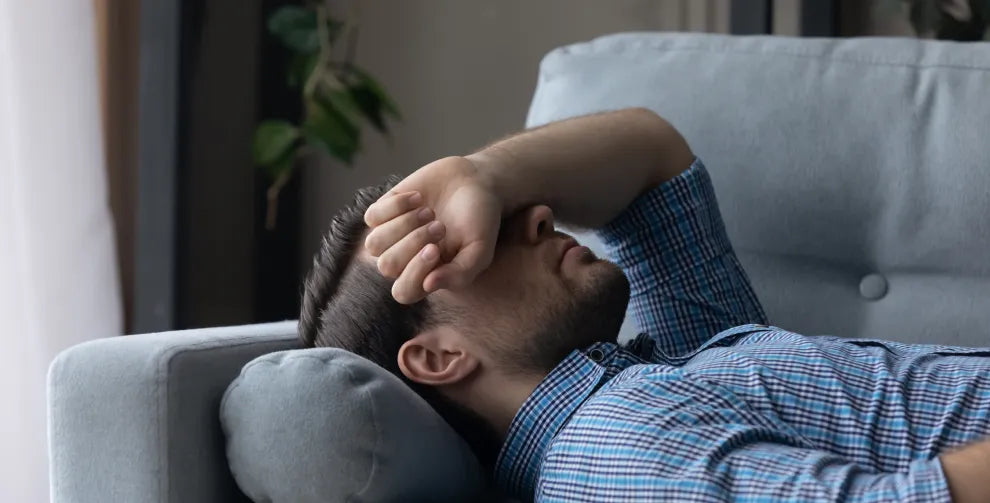
Migraines can interfere with work, daily responsibilities, and quality of life. Because of their intensity, those who experience them often search for ways to support their wellness and reduce the burden of recurring episodes.
This is where interest in CBD has grown. CBD, short for cannabidiol, is a naturally occurring compound found in the hemp plant. CBD has been the subject of growing research into its effects on the body’s regulatory systems.
This article explores what CBD is, how it works with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), what migraines are, what the science currently says about CBD and migraines, and how people may combine CBD with other supportive strategies.
What is CBD?
CBD is one of more than a hundred cannabinoids that naturally occur in the hemp and cannabis plants. These compounds interact with receptors in the body, often in complex and indirect ways. CBD itself does not bind strongly to the receptors most associated with the ECS, but is thought to influence them and other systems that help the body maintain balance.
Unlike hemp-derived THC, CBD is non-intoxicating. This distinction is one reason CBD has gained so much attention — it allows people to explore cannabinoid wellness without the altered mental state that THC can cause.
Products such as tinctures, gummies, and topicals have become some of the most popular ways people incorporate CBD into their daily lives.
What makes CBD even more intriguing is its versatility. Because the ECS is linked to processes like sleep, mood, and discomfort regulation, many people are curious about whether CBD could support areas of wellness that overlap with migraine experiences.
How does CBD work with the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids, which are compounds the body naturally produces. Its main role is to help regulate balance, or homeostasis.
When you feel stressed, tired, or out of sync, the ECS is part of what helps bring systems back into alignment.
There are two primary cannabinoid receptors in the ECS: CB1, found mostly in the brain and central nervous system, and CB2, found more commonly in immune cells. CBD doesn’t strongly activate these receptors.
Instead, it appears to work indirectly, possibly by slowing the breakdown of the body’s own endocannabinoids or by interacting with serotonin and TRPV1 (vanilloid) receptors, which are tied to stress response and discomfort perception.
Because migraines involve both neurological and physical pathways, affecting blood vessels, nerve signals, and serotonin activity, researchers are investigating whether CBD’s interactions with the ECS and related systems may be relevant for those who experience recurring episodes.
What are migraines?
Migraines are more than a typical headache. They are recurring episodes of intense head and neck tension that may last for hours or even days.
Along with discomfort, many people experience nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and fatigue. Some migraine sufferers even have warning signs known as auras, which can include visual changes or tingling sensations before an episode begins.
Triggers can vary widely from person to person. Common ones include:
- Stress or sudden changes in routine
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Skipped meals or certain foods (like aged cheeses, processed meats, and alcohol)
- Bright lights or strong smells
- Lack of sleep or irregular sleep patterns
- Dehydration
Because triggers are highly individual, migraine treatments often involve tracking patterns and making lifestyle adjustments to reduce their frequency. While conventional medications are often used, many people are also exploring supportive approaches to minimizing migraine symptoms.
CBD and migraines: what does the science say?
Research into CBD and migraine headaches is still in its early stages, but it is growing. Much of the existing work focuses on cannabinoids in general rather than CBD alone, but the findings are valuable for understanding where CBD might play a role.
Some studies suggest that the endocannabinoid system is involved in migraine processes. For instance, a clinical theory known as “endocannabinoid deficiency” proposes that people with recurring migraines may have lower levels of natural endocannabinoids, which could affect how their bodies regulate discomfort and neurological activity.
Early research shows that CBD may influence serotonin receptors, which are already known to play a role in migraine activity. Serotonin fluctuations are a key part of why migraines start and progress in the first place. By indirectly interacting with serotonin pathways, CBD may have potential relevance for future migraine studies.
However, it’s important to emphasize that most existing research is preliminary. While some small-scale human studies and reviews point to cannabinoids having a role in head and neck tension, large randomized controlled trials are still limited. More research is needed before clear conclusions can be drawn.
That said, growing scientific curiosity signals that the connection between CBD and migraine wellness is worth exploring further. People who are already interested in CBD often choose to incorporate it as part of a broader lifestyle plan rather than expecting it to act as a standalone measure.
What other methods may help with migraine discomfort?
Managing migraines often requires a holistic approach. CBD may play a role, but many people find that combining strategies works best.
Some complementary methods include:
- Hydration: Drinking enough water throughout the day is one of the simplest ways to reduce potential triggers.
- Sleep hygiene: Going to bed and waking up at consistent times helps the body maintain balance. Poor sleep is one of the most common migraine triggers.
- Balanced nutrition: Avoiding trigger foods and eating regular meals can help stabilize energy levels.
- Stress management: Practices like mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help calm the mind and body, potentially reducing the likelihood of an episode.
- Trigger awareness: Keeping a migraine diary can reveal patterns, making it easier to avoid common triggers.
- Medical treatments: Depending on the severity and frequency of your migraines, your doctor may recommend certain medications
CBD does not replace these approaches but may be considered alongside them to support overall wellness.
How to use CBD for best results
For those considering CBD as part of their migraine wellness strategy, it’s helpful to think about how it fits within a larger plan.
Popular CBD formats include tinctures and gummies, which are taken for general support, as well as topicals, which are applied directly to areas of tension. Choosing the right product often depends on individual preference and lifestyle.
Consistency matters. Many people notice subtle wellness effects when CBD is used regularly rather than occasionally. Serving size can also vary. What feels effective for one person may differ for another.
Starting low (5-10 mg) and increasing gradually each day until you feel the desired result is a common approach.
The bottom line
Migraines can have a major impact on daily life, and while conventional options exist, many people are curious about supportive wellness practices that go beyond traditional approaches. CBD is one of the most discussed supplements in this space, and research suggests it may have relevant interactions with systems tied to migraines.
While science is still evolving, CBD is often considered a supportive addition to a holistic routine that also includes hydration, sleep, nutrition, and stress management.
By combining these methods, individuals can create a wellness plan that addresses both immediate and long-term needs.
*This statement has not been evaluated by the Food & Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
FAQs
Can CBD stop a migraine once it starts?
Research is still too limited to say. CBD is not a treatment for migraines, but some people report using it to support relaxation and wellness during or between episodes.
Is CBD safe to use with other migraine remedies?
CBD is generally well-tolerated, but it can interact with some medications. Always consult with a healthcare provider before combining it with prescription or over-the-counter remedies.
What form of CBD is best for migraines?
There is no single best form. Tinctures and gummies are commonly used for overall wellness, while topicals may be applied to areas of localized tension.
How long does it take to notice effects from CBD?
It depends on the person, product type, and serving size. Some notice changes within days, while for others, consistent use over several weeks is needed to gauge full effects.
Sources:
The endocannabinoid system: Essential and mysterious | Harvard Health
Migraine: What It Is, Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatments | Cleveland Clinic